(Infectious Flexor Tenosynovitis)
Topic Resources
A bacterial infection can develop in the tendon sheath that surrounds the tendons in the palm and inside of the fingers.
Pockets of pus (abscesses) may occur around the tendons
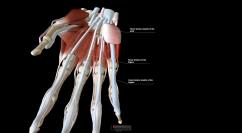
that run along the inside of the hand and fingers. These tendons are
inside a sleeve of tissue called the tendon sheath. The sheath helps the
tendons slide smoothly. A tendon sheath abscess is caused by an injury
that penetrates one of the creases on the palm side of a finger. Pus
from an untreated felon
may also spread from the tip of the finger into the end of the tendon
sheath. Infection and pus form around the tendon and rapidly destroy
tissue. The gliding mechanism of the tendon becomes damaged, so the
finger can barely move.
Symptoms of infection of the tendon sheath include swelling and
pain of the finger and tenderness over the tendon sheath. The finger
feels better when it is bent (flexed). Moving the finger can cause
extreme pain. Fever is common.
Flexor Tendon Sheaths of the Fingers
3D Model
Diagnosis
-
A doctor's examination
-
X-rays
-
Cultures
Doctors base the diagnosis of infection of the tendon sheath on an examination. They do x-rays to detect foreign bodies (such as a tooth fragment, needle, or other object) that may be hidden under the skin.
To identify the type of bacteria that is causing the infection,
doctors remove a sample of pus from the abscess and try to grow (culture) the bacteria in a laboratory.
Treatment
-
Drainage of pus
-
Antibiotics
The person is admitted to the hospital. Doctors drain the pus
through a surgical incision. Antibiotics are given by vein
(intravenously).











0 Comments